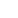Science in disguise: Robotic antelope roams with the herd in Hoh Xil
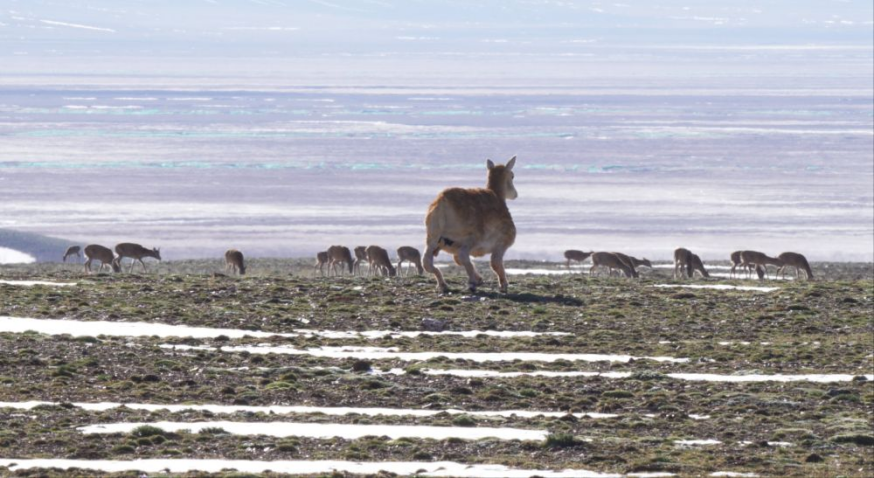

A robotic antelope (center) blends seamlessly into a herd of Tibetan antelopes. (Photo from the WeChat official account of DEEP Robotics)
At Zhuonai Lake in the remote wilderness of Hoh Xil, the northeastern part of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, a surprising newcomer recently appeared among a herd of Tibetan antelopes: a robotic replica. Moving naturally alongside the animals, the robot antelope was nearly indistinguishable from its living counterparts.
By allowing scientists to observe the herd at close range without disturbing it, the robotic antelope opens new possibilities for wildlife monitoring. Researchers at the Northwest Institute of Plateau Biology under the Chinese Academy of Sciences also expect it to collect droppings and placentas, providing more accurate and reliable data for behavioral and reproductive studies.
Hoh Xil, China's largest UNESCO World Natural Heritage Site, sits at an average altitude of over 4,500 meters. Its bitter cold, thin air, and vast uninhabited expanses form one of the harshest environments on Earth, yet it remains a sanctuary for rare species such as Tibetan antelopes and wild yaks.
The deployment of embodied-intelligence robots in wildlife conservation and ecosystem management illustrates how technological innovation is advancing ecological protection. Across China, breakthroughs in science and technology are increasingly aligned with efforts to protect the environment.
Sound conservation begins with thorough surveys and databases, where technology plays a central role. A team from the China Academy of Space Technology, for example, has built an integrated monitoring system that combines satellites with ground-based observations. The system tracks forests, crops, and water resources, generating critical data to guide ecological compensation for public-benefit forests and to assess the value of rural land-use rights.
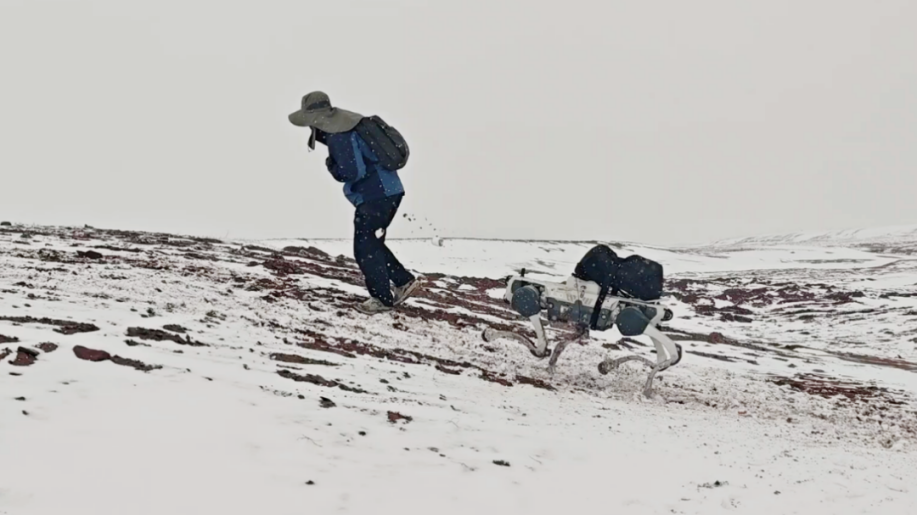

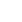
A researcher conducts fieldwork with a robot dog in Hoh Xil at 4,800 meters above sea levels. (Photo from the WeChat official account of DEEP Robotics)
Clean energy development is another cornerstone of ecological protection and green, low-carbon development. China is investing heavily in clean energy and low-carbon technologies. Recently, construction began on the nuclear island of Unit 1 at Jinqimen nuclear power plant in east China's Zhejiang province, equipped with the domestically developed Hualong One reactors. Once complete, the facility is expected to generate 55 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity each year.
At the 800-megawatt offshore wind project in Dafeng, east China's Jiangsu province, developed by China Three Gorges Corporation, the nation's first booster station equipped with a meteorological radar has just been installed. The project enables precise marine weather monitoring and more efficient offshore wind power generation, setting a benchmark for the development of offshore clean energy.
From advanced wastewater treatment and cleaner coal use to data-driven monitoring of vehicle emissions, technological solutions are essential to green development. At the Baihetan hydropower station, the world's largest clean energy corridor, a newly installed automated safety system now connects to more than 10,000 sensors. It continuously monitors deformation, seepage, stress, strain, and temperature, providing real-time analytics and early warnings to secure this massive renewable energy source.
New quality productive forces are inherently green productive forces. As scientific knowledge deepens and new technologies emerge, innovation will continue to drive ecological progress, building a greener, more sustainable home for all.
Photos
Related Stories
- Chinese surgical robot enables cross-continental operation
- Chinese robotics firms ramp up production amid accelerating commercialization
- Singing competition, horse race events held in NW China's Qinghai
- Interview: China carries torch for future "humanoid robot Olympics," says robotics expert
- A day in the life of a humanoid
- World's first humanoid robot games shine light on culture charm, tech applications
Copyright © 2025 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.