Chinese scientists confirm for the first time the presence of a solid inner core in Mars
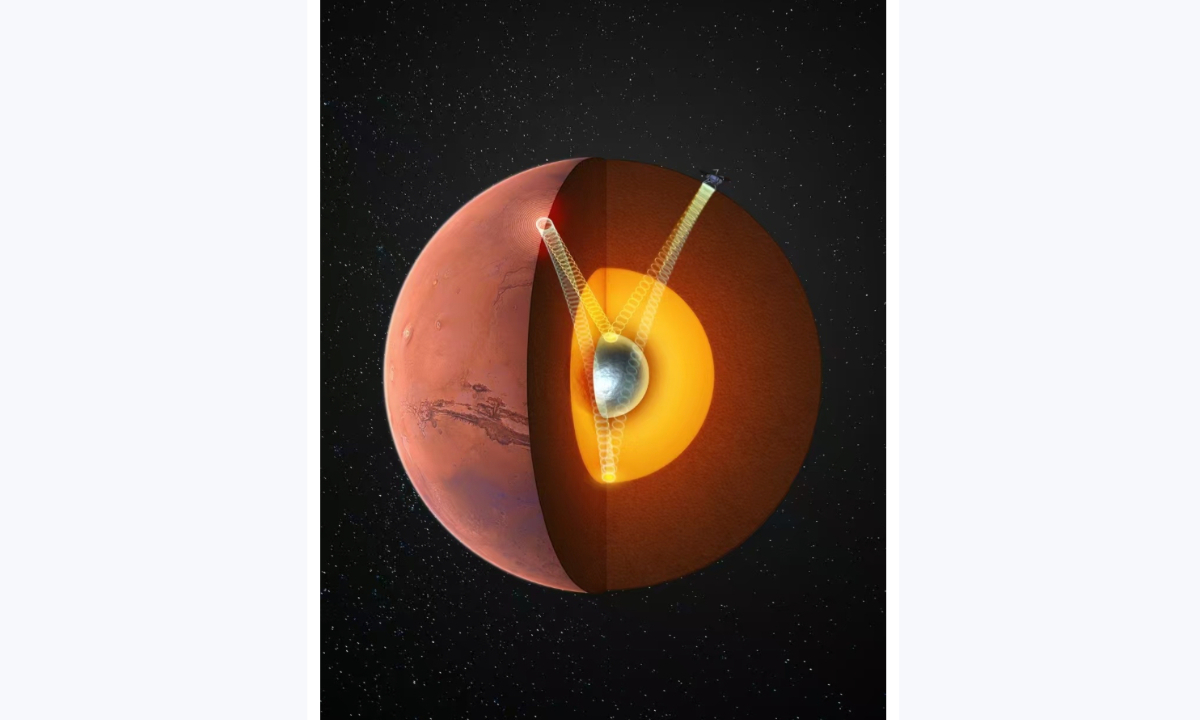

Photo: CCTV
Chinese scientists, together with international scholars, have for the first time confirmed the presence of a solid inner core in Mars with a radius of about 600 kilometers, a significant progress in planetary science research. Revealing its main composition provides important clues to the evolutionary process of Mars as well as Earth and other terrestrial planets, China Central Television reported on Thursday.
The research team led by Sun Daoyuan and Mao Zhu, professors from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), found that the main composition of the inner core in Mars is likely composed of crystalline iron-nickel alloy enriched with light elements. Their paper "Seismic Detection of a 600-km Solid Inner Core in Mars" was published in Nature on Wednesday.
As the solar system's terrestrial planet most similar to Earth in environment, Mars has long been central to studies of planetary interior structure and evolution, and is a core subject of deep space exploration. It was not until 1936 that scientists first inferred the existence of Earth's inner core through seismic waves, and it took scientists nearly half a century more, until the 1980s, to fully confirm that the inner core is solid, according to Sun, professor from the School of Earth and Space Sciences of the USTC.
By comparison, probing Mars' inner structure is even more difficult. Direct observational data of marsquakes were obtained for the first time only in 2018. Since then, more than a thousand marsquake events have been recorded, weak signals and noise interference still severely limit studies of Mars' deep interior, Sun told the Global Times on Thursday.
By analyzing marsquake data recorded by NASA's InSight lander, the research team successfully extracted key seismic phases that passed through Mars' core. Differences in these phases indicate that the core has a layered structure: an outer liquid core and a deeper solid inner core with higher wave velocities.
Further analysis identified, for the first time, evidence of a solid inner core within Mars and measured its radius at about 600 kilometers, accounting for one-fifth of Mars' total radius. If Mars were scaled up to the size of Earth, the proportion between its inner and outer core would be remarkably similar to Earth.
The team also found that Mars' core is not composed solely of iron and nickel, but may also contain 12 percent to 16 percent sulfur, 6.7 percent to 9 percent oxygen, and up to 3.8 percent carbon.
This inner core structure enriched with light elements not only provides important clues to the magnetic history of Mar - from being highly active in its early history to its present-day silence - but also lays a crucial foundation for comparing the internal evolution of Mars with that of Earth and other terrestrial planets.
This study confirmed, for the first time, the presence of a solid inner core in a planet beyond Earth, verifying that Mars has a core-mantle differentiation structure similar to Earth's. It marks a critical step forward for Chinese researchers in probing planetary interiors and highlights China's innovative capacity and international influence in cross-disciplinary research spanning planetary science and geophysics.
Nature reviewers praised the achievement, writing that "the authors have done a detailed job of using multiple lines of evidence for their phase detection analysis. Martian seismology is notably tough, so congratulations to the authors for doing such a thorough and careful job!"
Photos
Related Stories
- Chinese, international scientists reveal solid inner core in Mars
- Chinese team develops Mars soil simulant to boost future exploration endeavors
- China invites int'l partners on Tianwen-3 Mars sample-return mission
- China aims to carry out Mars sample return mission around 2030: NPC deputy
- Scientists provide evidence for existence of ancient ocean on Mars
- China's Mars rover Zhurong discovers evidence supporting ancient oceans existing in Mars' mid-latitude regions
- China's rover Zhurong helps find water-related features on Mars
- China aims to launch Mars sample-return mission around 2028
- Chinese scientists achieve major step toward Mars base construction
- New research suggests presence of concealed ocean beneath surface of Mars
Copyright © 2025 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.